Exome analysis with EAGLE
Investigators: Christopher Schröder, Felix Mölder & Sven Rahmann
Collaborators: Institute for Human Genetics, University Hospital Essen
Funding: Mercator Research Center Ruhr (2010-2012); now internal
Software: EAGLE
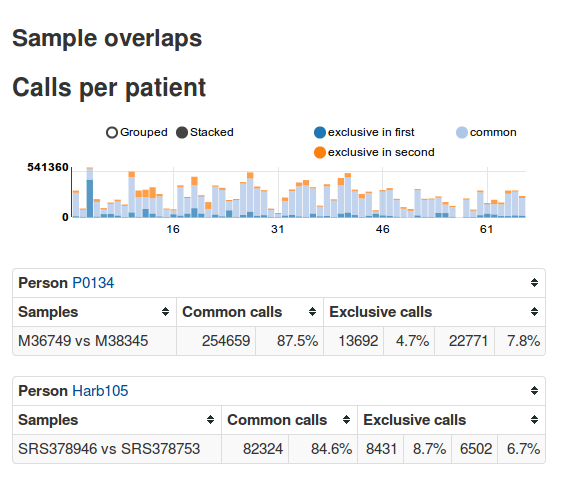
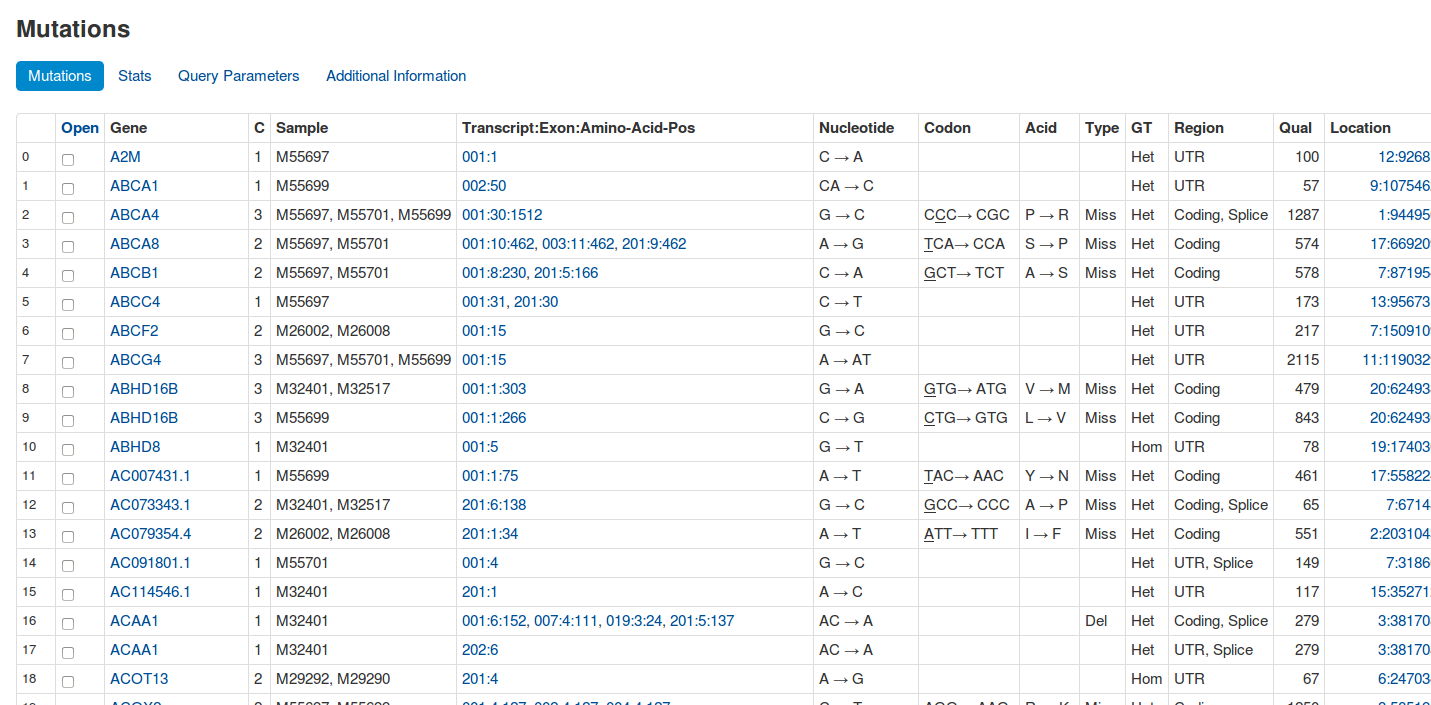
The aim of EAGLE is to identify disease-causing SNPs, copy number variations and structural variants by using exome sequencing data of tumor and blood or triples (index patient, father, mother), filter the data by official databases such as dbsnp and inhouse filter samples and show statistics to the end user.
EAGLE is an exome-sequencing pipeline with a web frontend. It automates most stepsfrom FASTQ files to variant calls, stores the calls and metadata about patients, samples, etc. in a database and allows interactive analysis via a web frontend. It is designed for easy use and has already been used in various studies [1, 2, 3].
EAGLE combines a best practices variant calling workflow, with a web frontend. By storing the called information in specifically structured and encapsulated HDF5 files (instead of a huge postgresql database), EAGLE allows filtering and parameter tuning in almost real time. This enables iterative tuning of thresholds, or the selection of different samples for filtering by the web interface.
References
[1] Martin, M. et al., 2013. Exome sequencing identifies recurrent somatic mutations in EIF1AX and SF3B1 in uveal melanoma with disomy 3. Nat. Genet. 45, 933–936.
[2] Czeschik, J.C. et al., 2013. Clinical and mutation data in 12 patients with the clinical diagnosis of Nager syndrome. Hum. Genet. 132, 885–898.
[3] Voigt, C., et al., 2013. *Oto-facial syndrome and esophageal atresia, intellectual disability and zygomatic anomalies - expanding the phenotypes associated with EFTUD2 hfg mutations. *Orphanet J Rare Dis 8, 110.
Algorithmic Bioinformatics, SIC, Saarland University | Privacy notice | Legal notice



